Health
Magnesium Benefits: for Men and Women Daily Needs

Magnesium is one of the most essential minerals for human health, yet it often remains overlooked in daily nutrition. While calcium and vitamin D are widely discussed, magnesium plays just as critical a role in maintaining healthy muscles, bones, heart function, and even mental balance. Recent studies have highlighted not only the well-known advantages of magnesium but also newly discovered benefits that emphasize its role in long-term wellness.
Both men and women require magnesium in slightly different amounts, influenced by biological needs, hormonal changes, and lifestyle factors. Men typically need magnesium to support muscle function, energy metabolism, and cardiovascular health. Women, on the other hand, benefit from magnesium for bone strength, hormonal balance, and reduced risks of migraines and anxiety.
This article explores magnesium benefits in detail, its daily requirements for men and women, food sources, supplementation, and how new research is shedding light on its broader role in health.
What Is Magnesium and Why Is It Important?
Magnesium is a vital mineral found in the earth, plants, and the human body. It functions as a cofactor in more than 300 enzymatic reactions, making it essential for energy production, protein synthesis, and nerve regulation. Without sufficient magnesium, the body cannot maintain stable blood sugar, proper nerve function, or muscle contraction.
Interestingly, recent findings show magnesium also plays a role in DNA repair and maintaining telomere length, which are directly linked to aging and longevity. This indicates that adequate magnesium intake might contribute to healthier aging.
Magnesium Benefits for Men
1. Supports Muscle Function and Recovery
For men, especially athletes and fitness enthusiasts, magnesium helps regulate muscle contractions, prevent cramps, and aid post-exercise recovery. Studies suggest that magnesium supplementation can improve endurance and strength by reducing lactic acid buildup.
2. Enhances Heart Health
Men are at higher risk of heart disease compared to women, and magnesium plays a protective role by helping regulate blood pressure, supporting healthy cholesterol levels, and preventing arterial stiffness.
3. Boosts Testosterone Levels
New research shows a direct link between magnesium intake and testosterone production. Higher testosterone supports muscle mass, energy levels, and reproductive health, making magnesium vital for men’s vitality.
4. Reduces Risk of Type 2 Diabetes
Magnesium improves insulin sensitivity, helping regulate blood sugar levels. Men with higher magnesium intake show a significantly lower risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Magnesium Benefits for Women

1. Improves Bone Density
Since women are more prone to osteoporosis, especially after menopause, magnesium supports calcium absorption and bone mineralization. This is crucial for long-term bone health.
2. Eases PMS and Menstrual Discomfort
Magnesium has been proven to alleviate premenstrual symptoms such as bloating, mood swings, and cramps. It helps regulate hormonal fluctuations and reduce inflammation during menstrual cycles.
3. Supports Pregnancy and Fetal Development
Pregnant women need higher levels of magnesium to support the growth of the fetus, prevent preeclampsia, and reduce risks of premature birth.
4. Reduces Stress and Anxiety
Magnesium has a calming effect on the nervous system, earning it the nickname “nature’s relaxant.” Women experiencing anxiety, insomnia, or hormonal stress often benefit from magnesium supplementation.
Daily Magnesium Needs: Men vs. Women
Magnesium requirements vary depending on age, gender, and health status.
-
Adult men (19–30 years): ~400 mg/day
-
Adult men (31+ years): ~420 mg/day
-
Adult women (19–30 years): ~310 mg/day
-
Adult women (31+ years): ~320 mg/day
-
Pregnant women: ~350–360 mg/day
-
Breastfeeding women: ~310–320 mg/day
These needs can often be met through a balanced diet, but due to modern lifestyle and dietary gaps, many people fall short.
Food Sources of Magnesium
Natural sources of magnesium are abundant and include:
-
Nuts and seeds: Almonds, cashews, pumpkin seeds, sunflower seeds
-
Leafy greens: Spinach, kale, Swiss chard
-
Whole grains: Brown rice, quinoa, oats
-
Legumes: Black beans, chickpeas, lentils
-
Seafood: Mackerel, tuna, salmon
-
Dark chocolate: High in magnesium and antioxidants
Eating a diet rich in these foods can help prevent magnesium deficiency.
Signs of Magnesium Deficiency
Magnesium deficiency is common, with up to 50% of adults in developed countries not meeting daily requirements. Symptoms include:
-
Muscle cramps and spasms
-
Fatigue and weakness
-
Poor sleep and insomnia
-
Irregular heartbeat
-
Headaches or migraines
-
Anxiety and irritability
If left untreated, chronic deficiency can lead to hypertension, osteoporosis, and metabolic disorders.
Supplementation: When and How?
While food is the best source, supplements can be beneficial for those with higher needs. Magnesium supplements come in different forms:
-
Magnesium citrate: Best for absorption and digestion support
-
Magnesium glycinate: Gentle on the stomach, good for anxiety and sleep
-
Magnesium oxide: Common but less bioavailable
-
Magnesium chloride: Effective for deficiency correction
Experts recommend taking magnesium with meals to improve absorption and reduce digestive discomfort.
Newly Discovered Insights on Magnesium Benefits
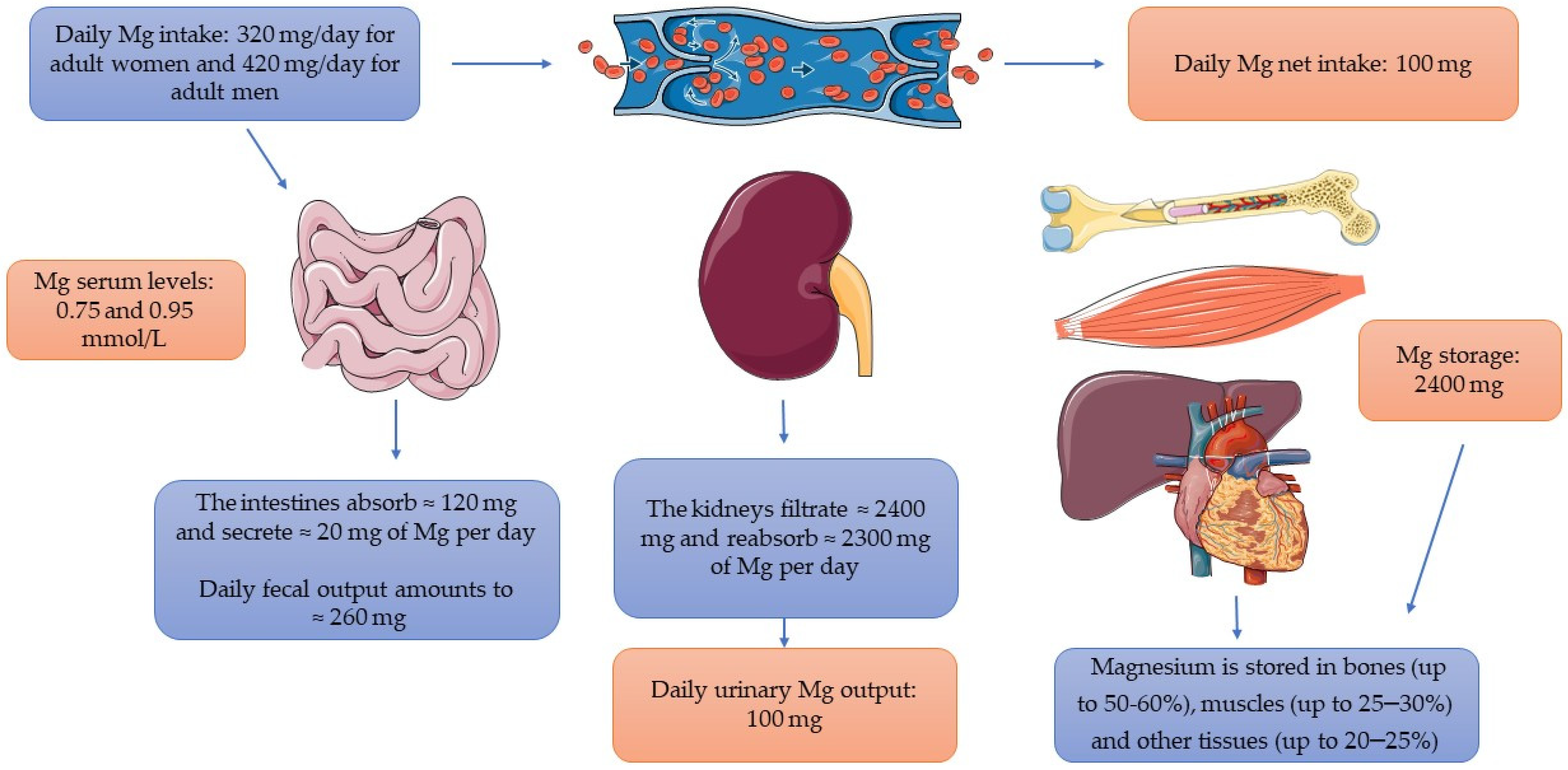
1. Role in Mental Health
Recent clinical studies have linked magnesium supplementation with significant reductions in depression and anxiety symptoms. Magnesium regulates neurotransmitters like serotonin, which influence mood stability.
2. Sleep Quality
New evidence shows magnesium’s role in supporting deep sleep cycles by activating the parasympathetic nervous system. This makes it a natural remedy for insomnia.
3. Inflammation and Immunity
Magnesium helps reduce chronic inflammation markers, which are associated with conditions like arthritis, obesity, and heart disease. Emerging research suggests magnesium also strengthens immune defense against infections.
4. Longevity and Aging
Scientists are now exploring magnesium’s impact on slowing cellular aging. By protecting DNA and supporting mitochondrial function, magnesium may help extend healthy lifespan.
Potential Risks of Excess Magnesium
While deficiency is common, excess magnesium from supplements can cause side effects such as nausea, diarrhea, and abdominal cramps. Extremely high doses can even affect kidney function. Therefore, supplements should only be taken under guidance if dietary intake is insufficient.
Conclusion
Magnesium is not just a basic mineral—it is a foundation for overall health. From muscle recovery in men to hormonal balance in women, magnesium plays a unique role in supporting daily wellness. New scientific findings reinforce its importance in mental health, longevity, and disease prevention.
Ensuring adequate magnesium intake—through a nutrient-rich diet or carefully chosen supplements—can enhance quality of life for both men and women.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are the top magnesium benefits for men?
Muscle recovery, testosterone support, heart health, and reduced diabetes risk.
2. Why do women need magnesium daily?
For bone density, menstrual relief, pregnancy health, and stress management.
3. Can magnesium help with sleep problems?
Yes, magnesium supports deep sleep cycles and helps calm the nervous system.
4. What foods are highest in magnesium?
Leafy greens, nuts, seeds, whole grains, legumes, and dark chocolate.
5. How do I know if I am magnesium deficient?
Look for signs such as cramps, fatigue, poor sleep, headaches, and irritability.
6. Is it safe to take magnesium supplements daily?
Yes, when taken within recommended doses, supplements are generally safe.
7. Can too much magnesium be harmful?
Yes, excessive supplementation may cause digestive issues and kidney strain.
-

 Celebrity8 months ago
Celebrity8 months agoNick Schmit? The Man Behind Jonathan Capehart Success
-

 Celebrity9 months ago
Celebrity9 months agoChristina Erika Carandini Lee: A Life of Grace, Heritage, and Privacy
-

 Celebrity9 months ago
Celebrity9 months agoTrey Kulley Majors: The Untold Story of Lee Majors’ Son
-

 Celebrity9 months ago
Celebrity9 months agoJamie White-Welling: Bio, Career, and Hollywood Connection Life with Tom Welling
















